Disclaimer: The Blog on ‘Edible Oil’ is not a recommendation to buy / hold / sell any stock. Please read the detailed disclaimer at the bottom of the post.
Edible Oil Manufacturing Process
The production process of vegetable oil involves the removal of oil from plant components, typically seeds. This can be done via mechanical extraction using an oil mill or chemical extraction using a solvent. The extracted oil can then be purified and, if required, refined or chemically altered.
Mechanical Extraction: Generally termed “crushing” or “pressing.” India uses Ghani method.
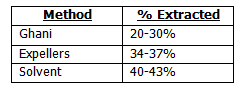
Solvent Extraction: The processing of vegetable oil in commercial applications is commonly done by chemical extraction, using solvent extracts, which produces higher yields and is quicker and less expensive. The most common solvent is petroleum-derived hexane. This technique is used for most of the “newer” industrial oils such as soybean and corn oils.
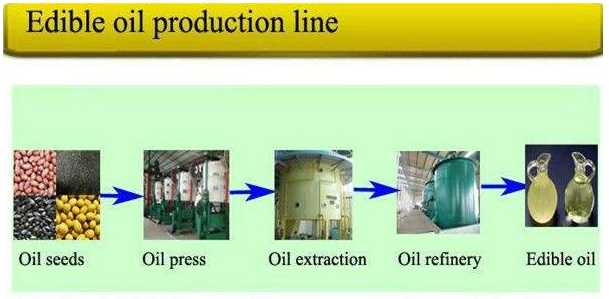
(Source – dhanyam.in )
Oil Seeds Production
Oil Seed crops are second most determinant category of crops for our agricultural economy, post cereals. The self-sufficiency in oilseeds attained through “Yellow Revolution” during early 1990’s, could not be sustained beyond a short period.
Usage of Oilseeds : Usage can be broadly divided into 2 categories –
- Crushing Industry: Crushing of oilseeds into vegetable oils.
- Edible Seed Industry: It can be divided into 2 sub-groups –
- Food Manufacturing: Used as ingredients by various food manufacturing industries and are further segmented into food processing (e.g. spreads and sauces) and snacks.
- Confectionery: Used as a topping on breads, bakery products and confectionery to enrich their appearance and texture.
Global Historical Oil Seeds production
Global oilseed production has been growing at ~3.2% CAGR since 2006 and has reached .
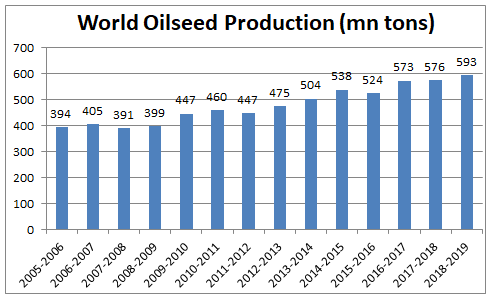
(Source – http://www.sopa.org/statistics/)
Historical Oil Seeds production in India
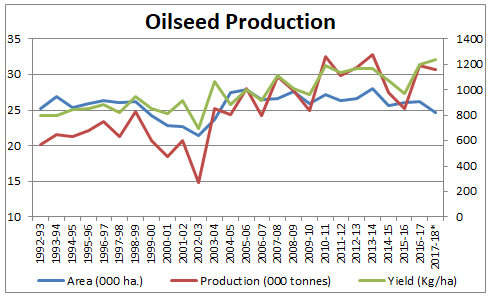
(Source – NMOOP2018)
We can see over last 25 years, how the land area under oilseed production has not grown meaningfully. So, whatever increase in our oilseed production has occurred in India is mainly because of our improvement in the crop yields (kg/ha or tons/ha). However, our yields are still nowhere close to the world average yields, leave aside the world best yields.
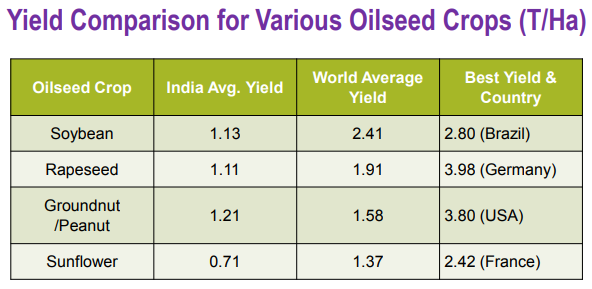
(Source – India’s Edible Oil Demand & Supply Situation by Vijay Sardana)
Global Oilseed Production Over Time Based On Types Of Oilseeds
Soybean is the most produced oilseed globally.
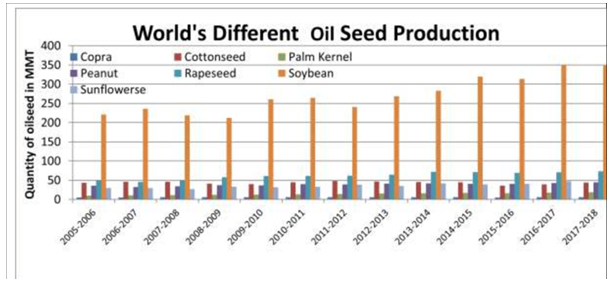
(Source – Researchgate by Siba Prasad Mishra)
Oilseed Production Over Time Based On Types Of Oilseeds In India
We can see how over the last decade Sunflower oilseed production has consistently reduced and remaining oilseeds also haven’t seen any significant growth.
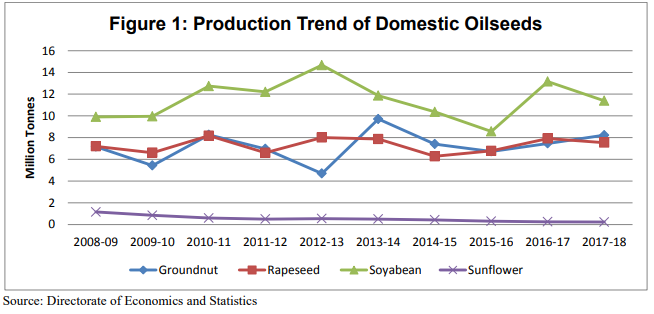
(Source – Commodity Profile of Edible Oil for April – 2018)
Geographic Distribution Of Oil Seeds In India
Oilseed production is quite concentrated in some states in India. Madhya Pradesh accounts for 27% of the production and top 4 states account for ~80% of the production.
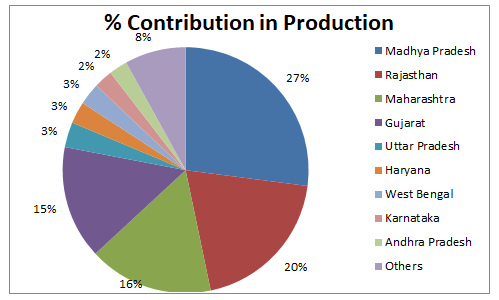
(Source – Presentation on Vegetable oils vis-a-vis Soybean in India by DAC&FW)
Edible Oil Consumption in India
Breakup of Production Based On Oil Type
Palm oil forms a major share of the edible oil consumed by Indians, with second most consumed oil being Soyabean Oil. Together both sum up to ~65 % to 75 % of our consumption.
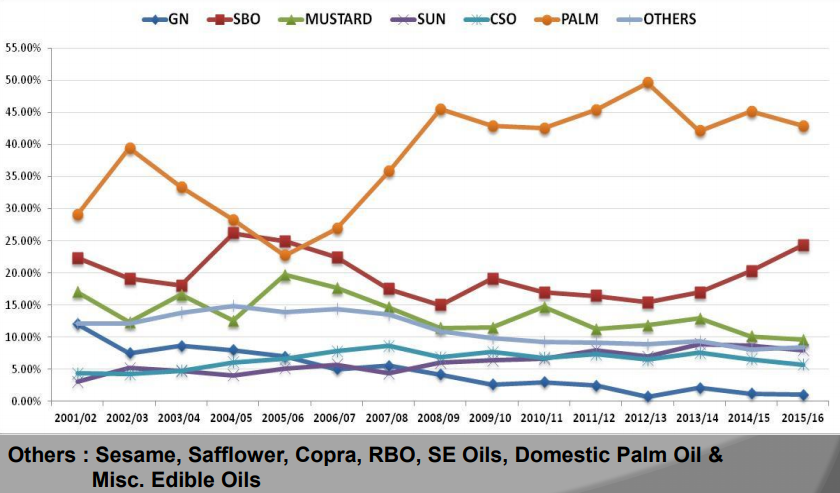
(Source – Indian Edible Oils Demand & Supply And Outlook for 2016-17 by Govindbhai G. Patel)
Geographical Breakup Of Edible Oil consumption
Edible Oil consumption is somewhat higher in Western India and lesser in Southern India, however more or less it’s proportional to the population distribution. On comparative basis, Palm oil is not much favoured by North India, whereas South India has preference for Sunflower oil and they are lesser inclined towards Soybean oil and Mustard oil.
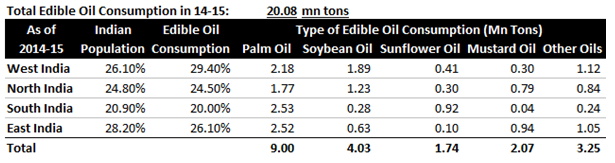
(Source – Indian Edible Oils Demand & Supply And Outlook for 2016-17 by Govindbhai G. Patel)
Supply And Demand Of Edible Oil In India
Major part of our Edible Oil demand has been supported by equivalent increase in imports. Since 2012-13, out of the 6 mn tons of incremental demand has parallely seen 5 mn tons of import increment. At the same time, import as % of demand has increased from 55% to 59%.
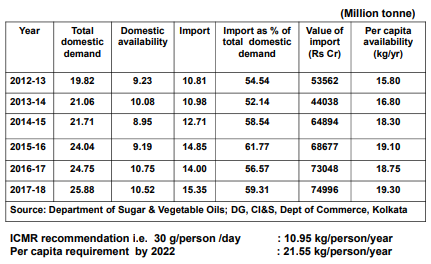
(Source – Presentation on Vegetable oils vis-a-vis Soybean in India by DAC&FW)
Import Of Edible Oils In India
Indian edible oil import has grown at 8.4% CAGR over last decade. Broadly, the portion of refined oil in the imports has been ~15% of the total imports. The remaining crude (non-refined) edible oil imported is refined in local units. The existing duty differential between CPO (crude palm oil) and RBD (refined, bleached, and diodized) stands at 7.5%, which provides protection to domestic refiners against competition from imported refined oils to certain extent.
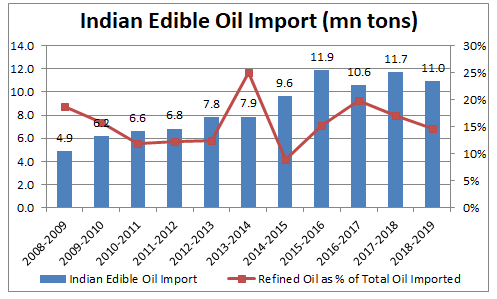
(Source – http://www.sopa.org/statistics/)
Import Breakup Of Edible Oil In India
Palm oil has been the main edible oil imported in India. Off lately, Soybean oil imports have also increased sharply.
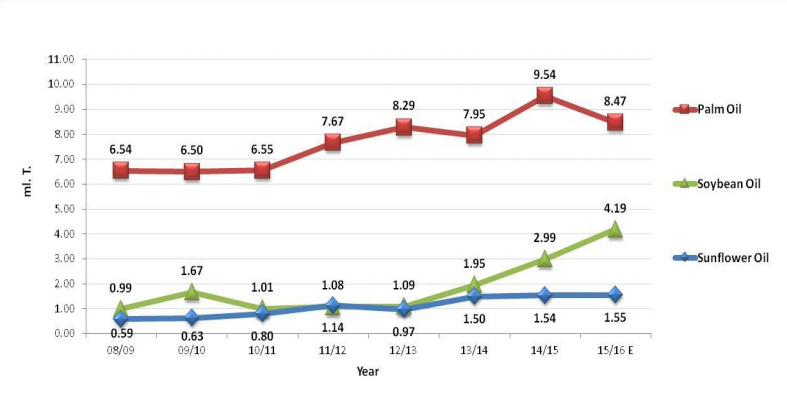
(Source – Indian Edible Oils Demand & Supply And Outlook for 2016-17 by Govindbhai G. Patel)
Vegetable oils form over half of the total Agricultural import in India. Despite being the 5th largest oilseed crop producing country in the world, India is also one of the largest importers of vegetable oils today. Our Edible Oil import bill comes at around Rs. 70,000 cr annually! It is one of the low hanging fruit for the government to improve our forex reserves.
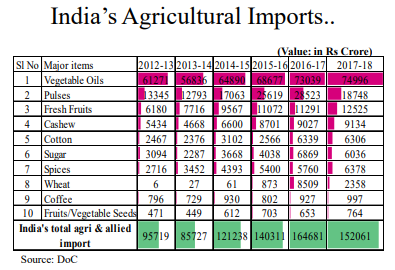
At the same time, it forms very miniscule part of our exports
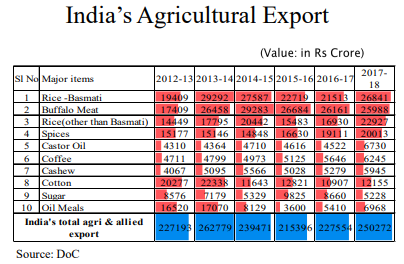
Indian Edible Oil Structure
Due to this heavy import of edible oil, the existing Indian mills are operating at very low utilisations.
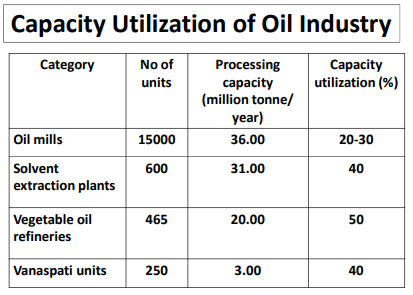
(Source – Presentation on Vegetable oils vis-a-vis Soybean in India by DAC&FW)
Import Duties
We can see how import duty has decreased dramatically for all types of oil from ~70% to existing 15-20%, which has made importing edible oils even more viable.
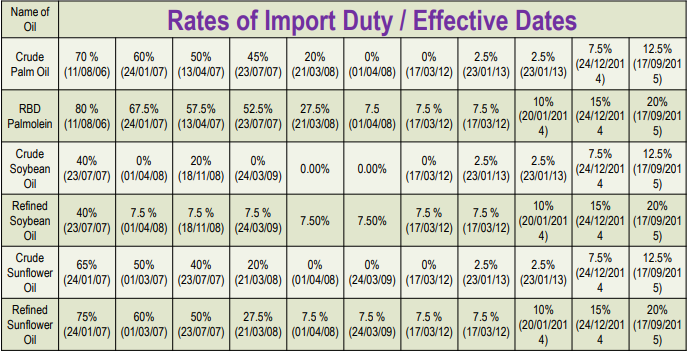
(Source – India’s Edible Oil Demand & Supply Situation by Vijay Sardana)
What Happens If We Improve Our Farm Yields?
A simple calculation shows that if our yield improves from existing case to even global average yields, Indian edible oil production would grow by 67% to ~13.5 mn tons on the same area of cultivation. And if our yields improve to global best rates, Indian edible oil production would become 3x the existing 8-9 mn tons production and India will be self-sufficient on existing cultivated land itself!
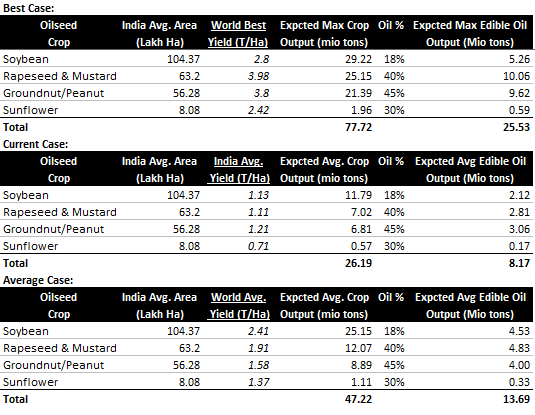
Constraints for increasing oilseed production are as following:
- External price shock on account of dependence on import is a major challenge in this sector
- The cultivation of oil seed farms such as palm has long gestation period of about 3-7 years before the cultivators could actually begin to derive benefit from thereof.
- Oilseed crops are largely grown under rain-fed condition (>70%) and are more prone to biotic and a-biotic stresses. Only one fourth of oilseed producing area remains under the irrigation.
- High seed rate (number of seeds (Kg) to be used per hector or acre for maximum yield) and cost of seeds coupled with non-availability of quality seeds of varieties and hybrids.
Oilseed Meal
It is a meal made from the residue of pressed oilseeds, most commonly used as animal feed or fertilizer
- India’s lower oilseed production has in recent years increased the country’s import needs for vegetable oils. However, it is also causing considerable change to the oilseed meal balance of trade. Historically, India has exported any oilseed meal that is not used domestically.
- Traditional Indian export destinations such as Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam etc. are switching to lower priced origins due India’s uncompetitive pricing in export markets. Further reductions in demand come from Iran, which after the lifting of trade sanctions, is now able to buy from cheaper origins. Japan has also now started using GM soyabean meal, which reduces the demand for Indian non-GMO soyabean meal.
Export of Oilmeal has reduced off lately.
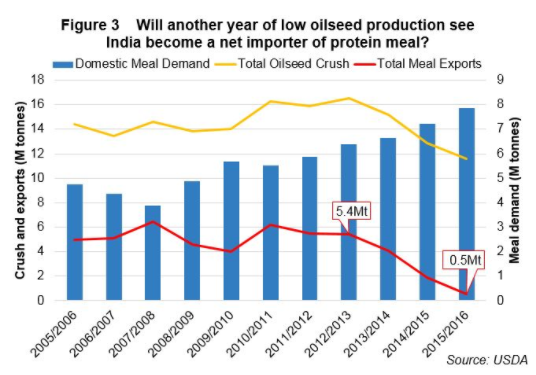
(Source – India’s evolving vegetable oil and oil meal trade balance)
Subscribe to our WhatsApp and receive updates directly:
Disclaimers :
The information herein is used as per the available sources of bseindia.com, company’s annual reports & other public database sources. Alpha Invesco is not responsible for any discrepancy in the above mentioned data. Investors should seek advice of their independent financial advisor prior to taking any investment decision based on this report or for any necessary explanation of its contents
Future estimates mentioned herein are personal opinions & views of the author. For queries / grievances – support@alphainvesco.com or call our support desk at 020-65108952.
SEBI registration No : INA000003106
Readers are responsible for all outcomes arising of buying / selling of particular scrip / scrips mentioned here in. This report indicates opinion of the author & is not a recommendation to buy or sell securities. Alpha Invesco & its representatives do not have any vested interest in above mentioned securities at the time of this publication, and none of its directors, associates have any positions / financial interest in the securities mentioned above.
Alpha Invesco, or it’s associates are not paid or compensated at any point of time, or in last 12 months by any way from the companies mentioned in the report.
Alpha Invesco & it’s representatives do not have more than 1% of the company’s total shareholding. Company ownership of the stock : No, Served as a director / employee of the mentioned companies in the report : No. Any material conflict of interest at the time of publishing the report : No.
The views expressed in this post accurately reflect the authors personal views about any and all of the subject securities or issuers; and no part of the compensations, if any was, is or will be, directly or indirectly, related to the specific recommendation or views expressed in the report.
Stay Updated With Our Market Insights.
Our Weekly Newsletter Keeps You Updated On Sectors & Stocks That Our Research Desk Is Currently Reading & Common Sense Approach That Works In Real Investment World.
