Disclaimer: The Blog on ‘Cloud’ is not a recommendation to buy / hold / sell any stock. The published post is for information purpose only. Please read the detailed disclaimer at the bottom of the post.
What is Cloud Computing?
The term cloud has now become synonymous with Internet. On similar grounds, Cloud Computing is the idea of utilizing resources spread over a network to achieve a collective goal.
The vertical has evolved over time and created three major buckets under which a company falls. Typically, the grouping depends on the type of service provided by the firm. These are also known as delivery models of cloud computing.
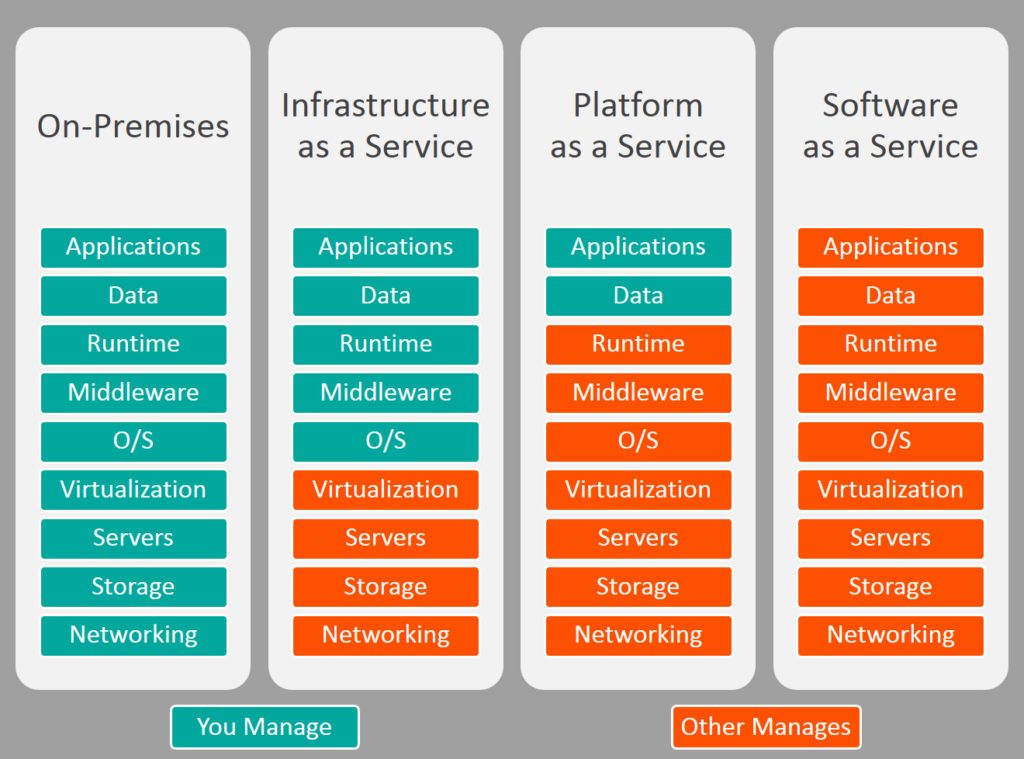
Classification on The Basis of Services
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (Paas)
- Infrastructure as a Service (Iaas)
Each model is an abstraction layer encapsulating the next model. To explain in simple words, imagine a hypothetical situation wherein you are in Pune and have to meet an old friend of yours who lives in Mumbai. You have four options:
| Task | Model | Pricing | Notes |
| Get in a bus | Saas | You pay for what you use, i.e. a single ticket to Mumbai | Low customization possible. You cannot reroute and visit Lonavala. Scaling managed automatically. More customers will result in more buses. |
| Hire a taxi | PaaS | You pay for the distance run, i.e. Pune to Mumbai approx 150 kms x rate per km | You can visit Lonavala, but cannot keep the vehicle waiting indefinitely. |
| Rent a car | IaaS | You pay a daily rental | Customizable to a large extent, can do whatever you want. Scaling managed by end user. More passengers would require you to rent more cars in advance. |
| Drive your own car | – | You are the owner of infrastructure | Fully customizable. |
To bring the discussion more inline with technology, essentially every software needs some kind of hardware to run. Consider a case where an owner of a small scale enterprise wants to have his own website to increase awareness and receive long distance orders. Specifically, he wants a website developed using WordPress. WordPress is a framework and needs PHP libraries to run on. PHP is a language designed for web development and needs an OS, example Windows.
Firms offering cloud Windows machines are IaaS providers. (sellers of Infrastructure)
Firms offering PHP Bridges and need only code to execute are PaaS providers. (sellers of Platform)
Firms offering WordPress website hostings are SaaS providers. (sellers of Software)
| Service | Players | Customers | USP |
| SaaS | Freshdesk, Zoho, Salesforce | Businesses | Product idea, innovation |
| PaaS | AWS Lambda, Google AppEngine | Software developers building products on common stack | Scaling, Ease of use |
| Iaas | AWS EC2, E2E | Software developers building custom products / custom use | Cost leadership, Server reliability |
Source: https://www.bmc.com/blogs/saas-vs-paas-vs-iaas-whats-the-difference-and-how-to-choose/
Key Drivers of The Industry:
- Surge in internet penetration in Tier II and III cities
- Many small & medium businesses are coming online and utilizing cloud platform
- Regulations around data localization
- R&D in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and IOT based products
- Government policies to push digitization
- Digital marketing and advertising
Global Players (The Big Five)
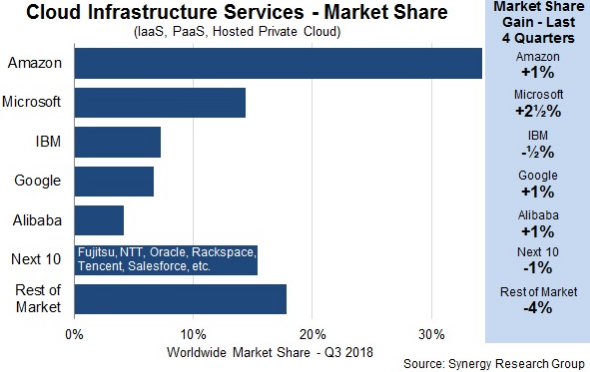
Cloud infrastructure services market is dominated by Amazon followed by Microsoft, IBM, Google and Alibaba. Together, the top 5 have captured more than 60% of the pie.
Projected Growth of Industry
| million USD | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Cloud Business Process Services (BPaaS) | 88 | 113 | 145 | 186 | 236 |
| Cloud Application Services (SaaS) | 396 | 527 | 675 | 824 | 1006 |
| Cloud Application Infrastructure Services (PaaS) | 107 | 141 | 182 | 230 | 287 |
| Cloud System Infrastructure Services (IaaS) | 486 | 725 | 1051 | 1473 | 2028 |
| Cloud Management and Security Services | 116 | 152 | 190 | 234 | 281 |
| Cloud Advertising | 123 | 158 | 189 | 223 | 266 |
| Total | 1316 | 1817 | 1432 | 3169 | 4104 |
Source: http://www.gartner.com/newsroom/id/3592917
The highest growth is driven by Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). The increase of SaaS and PaaS are indicators that the migration of application and workloads from on premises data centres to the cloud, as well as the development of cloud ready and cloud native applications are fuelling the growth in the cloud space.
Infrastructure As a Service
The focus of this blog will remain on IaaS providers since I believe cloud tech is slowly becoming a commodity and price differentiation plays a key role in shaping the industries in such a scenario. India, being a developing country and access to latest technology has an advantage over global players considering real estate, employee costs and other major expenses.
The primary role of an IaaS provider is to lease high density racks from a managed infrastructure services company (e.g. Netmagic) and create sub system or virtual machines which are available for rent to end users. How it does that? It deploys what is known as a Hypervisor to create, run and monitor virtual machines.
A Hypervisor has the responsibility of creating multiple guest virtual machines which share the system’s resources. Effectively, it is synonymous to having multiple operating systems on the same computer hardware but they all have the capability and capacity to run in parallel.
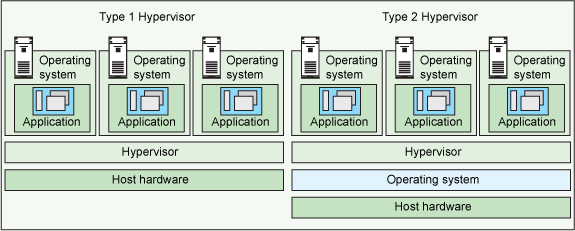
There are broadly two types of hypervisors, namely Type I and Type II.
Type 1 hypervisors are more common in service providers wherein they run directly on top of supplied hardware without the need of an operating system or other software. Operating systems although can be installed in a guest VM created by Type 1 hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisors are used in managing virtual machines in IaaS providers.
Type 2 hypervisors, also known as hosted hypervisors are more commonly in personal computers. VmWare or VirtualBox which is used to run another OS in our personal computers is a very popular example of type 2 hypervisor.
Source: https://vapour-apps.com/what-is-hypervisor/
Performance Metrics In IaaS Products
Typically, a shared server is also measured with the same parameters used to compare retail personal computers. Metrics which are in control of service provider and are commonly observed:
- CPU cores -Measured in a quantum of virtual cores.
- RAM
- Storage capacity
There are some metrics generally ignored but are taken into consideration by some serious customers. Majority of these metrics are not in control of service providers since they don’t own the hardware.
1] CPU Generation –
Latest generation processors often provide better performance as compared to older generation processors.
2] Network Bandwidth Throughput & Latency –
Network speed is an important metric to consider if the heavy data inflow or outflow is present.
3] Storage Read/Write Speed –
Use cases like generating analytics requires heavy read / write of data on and from the storage medium.
4] Storage Type – SSD / Magnetic Disks –
Magnetic disks are almost non existent in data centers nowadays. SSD provide much better throughput.
Why Service Providers Lease Hardware
1] Low Upfront Cost –
A big chunk of expense for a firm is dedicated for building tech infrastructure. Leasing is an attractive option especially for small scale players since it keeps operating expenses and cash flow in control.
2] Frequently Evolving Technology-
“The number of transistors incorporated in a chip will approximately double every 24 months.”—Gordon Moore, Intel co-founder
IT hardware manufacturers are bringing innovation in improving efficiency, lowering costs and power dissipation at a staggering rate. A new product lineup is available from the same manufacturer almost every new year.
The processors manufactured by Intel, which is a leader in providing desktop CPUs, way back in 2004 were built on 45nm technology. It has shrunk to 10 nm in 2017.
3] Flexible Load –
Since the hardware is leased, there are low unused resources or servers sitting idle. Scaling with customer base is easy as compared to wholly own the hardware and manage it.
Headwinds To The Industry
1] Highly Dependent on Data Centers –
Majority of the players in the industry enter into a lease agreement to supply infrastructure. Due to this fact, there is less control over the product which is used by the end user.
2] Reliability, Quality of Service –
The firms also have to maintain a service level agreement of providing upwards of 99% (typical) uptime guarantee. Frequent disruptions in network or connectivity will cause loss in faith of the customers.
3] Cost Limitation-
A large portion of the market is cost conscious.
Ongoing Debate : Will Paas Eat Up IaaS Demand
There are lots of discussions flooding in the internet about PaaS companies. Many web development firms are moving away from managing shared servers to PaaS providers like AWS Lambda and Google AppEngine. Reasons revolve around high overheads involved in managing resources and paying for unused capacity. But the decrease in demand due to these reasons is overshadowed by the cumulative growth in industry as a whole. Moreover, majority of the custom implementation of stacks still require a dedicated server and PaaS frameworks are not yet evolved which can undertake all the use cases.
Key Terms:
| Rack | A rack, in an IT context, is a supporting framework that holds hardware modules. In this context, racks typically contain servers, hard disk drives and other computing equipment. Racks make it possible to contain a lot of equipment in a small physical footprint without requiring shelving. |
| Bare metal server | A bare metal server is a physical server dedicated to a single tenant. The server’s tenant can optimize the server according to its needs for performance, security and reliability. The alternative to a bare metal server is a hypervisor server, in which multiple users share a virtual server’s compute, storage and other resources. |
| Hypervisor | A hypervisor is an operating system / software that can create virtual machines (VM) within a bare metal server. Can be classified as a Type 1 or Type 2 Hypervisor based on abstraction level. |
| Virtual machine | A virtual machine is a computer file, typically called an image, which behaves like an actual computer. In other words, creating a computer within a computer. It runs in a window, much like any other programme, giving the end user the same experience on a virtual machine as they would have on the host operating system itself. The virtual machine is sandboxed from the rest of the system, meaning that the software inside a virtual machine cannot escape or tamper with the computer itself. |
| Nm (45 nm) | The size of the features (the elements that make up the structures on a chip) are measured in nanometers. A 22 nm process technology refers to features 22 nm or 0.22 µm in size. Also called a “technology node” and “process node,” early chips were measured in micrometers |
Outlook
Public Cloud Computing industry is growing at a fast rate. Global leaders like Amazon, IBM will be the market makers but many local players are competing by providing price differentiation to customers. Amidst rapidly evolving technology, the stakeholders must ensure that they are in the forefront in adopting latest technology and maintaining the costs under a level.
Disclaimers :
The information herein is used as per the available sources of bseindia.com, company’s annual reports & other public database sources. Alpha Invesco is not responsible for any discrepancy in the above mentioned data. Investors should seek advice of their independent financial advisor prior to taking any investment decision based on this report or for any necessary explanation of its contents
Future estimates mentioned herein are personal opinions & views of the author. For queries / grievances – support@alphainvesco.com or call our support desk at 020-65108952.
SEBI registration No : INA000003106
Readers are responsible for all outcomes arising of buying / selling of particular scrip / scrips mentioned here in. This report indicates opinion of the author & is not a recommendation to buy or sell securities. Alpha Invesco & its representatives do not have any vested interest in above mentioned securities at the time of this publication, and none of its directors, associates have any positions / financial interest in the securities mentioned above.
Alpha Invesco, or it’s associates are not paid or compensated at any point of time, or in last 12 months by any way from the companies mentioned in the report.
Alpha Invesco & it’s representatives do not have more than 1% of the company’s total shareholding. Company ownership of the stock : No, Served as a director / employee of the mentioned companies in the report : No. Any material conflict of interest at the time of publishing the report : No.
The views expressed in this post accurately reflect the authors personal views about any and all of the subject securities or issuers; and no part of the compensations, if any was, is or will be, directly or indirectly, related to the specific recommendation or views expressed in the report.
Stay Updated With Our Market Insights.
Our Weekly Newsletter Keeps You Updated On Sectors & Stocks That Our Research Desk Is Currently Reading & Common Sense Approach That Works In Real Investment World.